The Apple Swift AWS Lambda Runtime is finally a reality, and it’s now officially supported (as announced May 29). The key fact that allowed this is the support for the Amazon Linux 2 with a custom Docker image maintained by Swift.
This article will show how to implement a basic REST API using the new Apple runtime to implement a serverless stack based on API Gateway, Lambda, and DynamoDB and deploying it using the Serverless Framework.

Serverless API Rest Architecture
This project uses the classic serverless architecture, which is based on:
API Gateway: Acts as aproxyfor theLambdaand exposes it to the internetLambda: The stateless computational layer. We defined a lambda for each API endpoint.DynamoDB: The AWSNoSQLdatabase providing data persistency

Advantages of a serverless architecture:
- Pay per use
- No fixed costs
- Autoscaling
- DevOps
The deployment file, serverless.yml, contains all of the details needed to deploy the example using the Serverless Framework.
Project Setup
We’re assuming you have followed the README to set up all of the requirements:
- AWS CLI configured with your AWS account
- Docker
- Serverless
- Make
Getting Started
Clone the template project:
git clone https://github.com/swift-sprinter/aws-serverless-swift-api-template.git
cd aws-serverless-swift-api-template.git
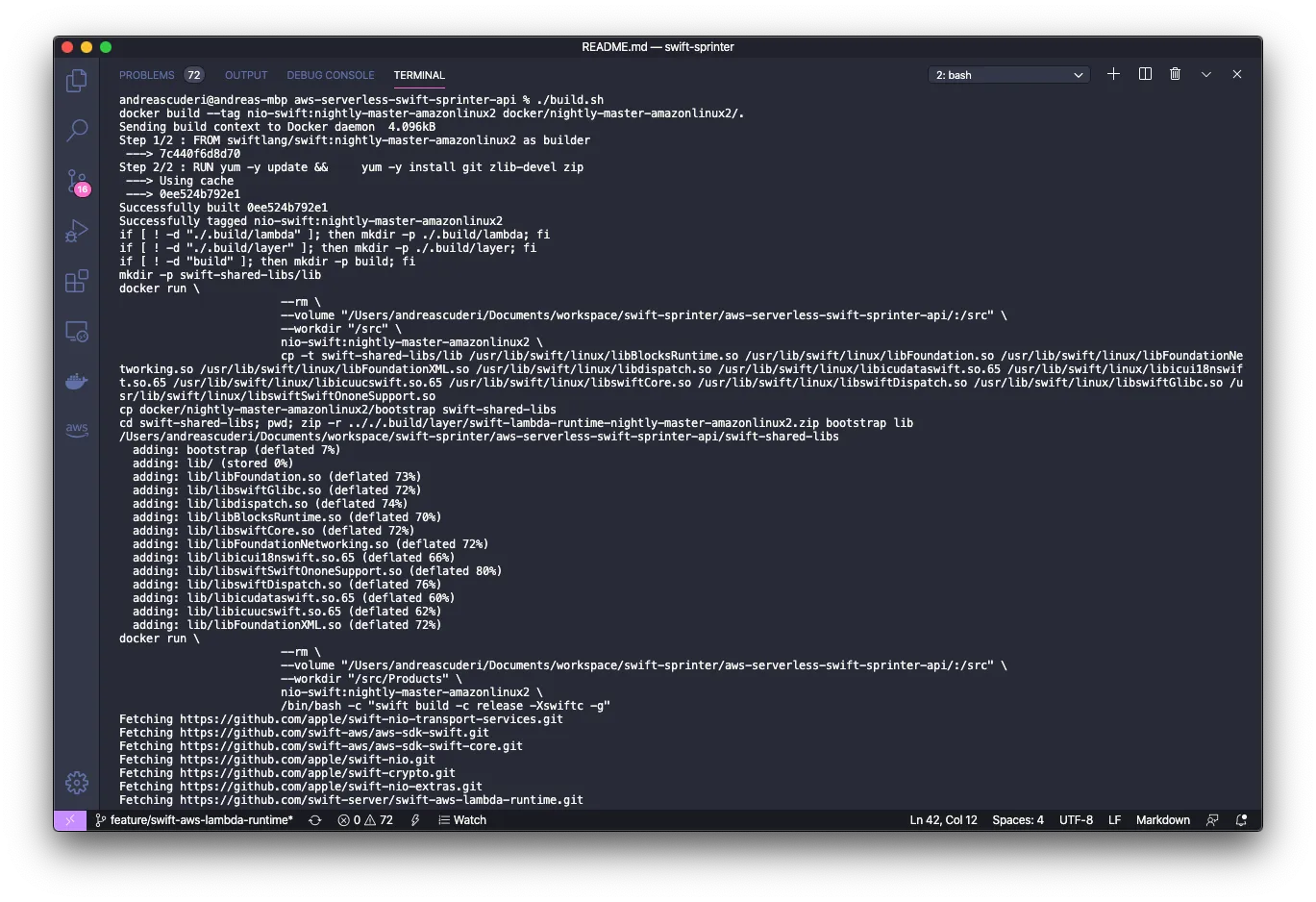
Then, build the project:
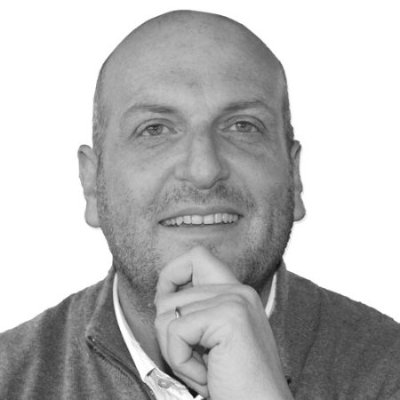
./build.sh
./deploy.sh
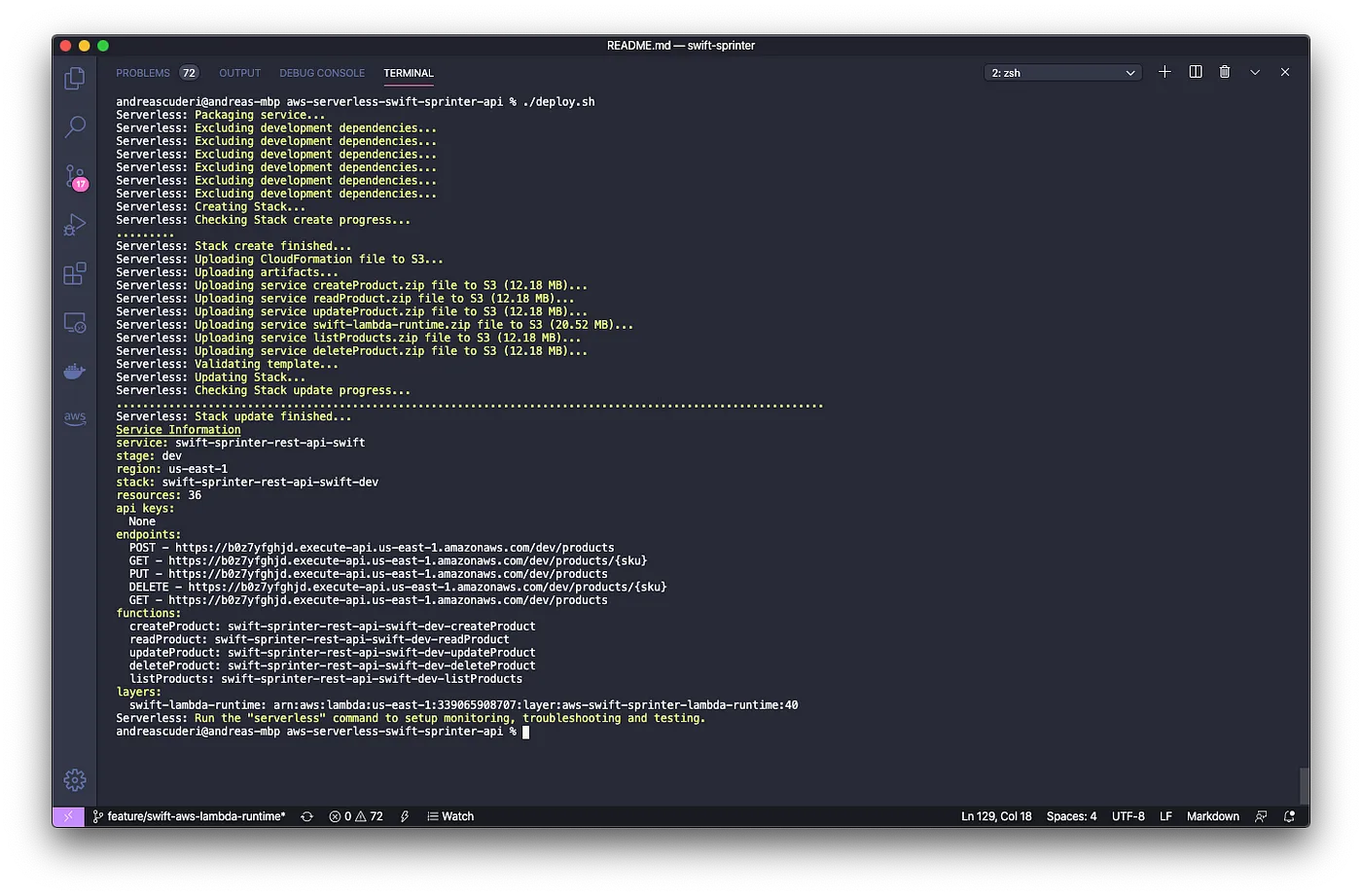
Once the project is deployed on your AWS account, the endpoints are created.
If everything is correct, the Serverless Framework will output the API endpoints.
API Testing With Postman
Take note of the base URL of the endpoints:
https://<api_gtw_id>.execute-api.<aws_region>.amazonaws.com/dev
<api_gtw_id> is the identifier for the API gateway generated by the script in the region <aws_region>.
Import the file swagger.json with Postman, and edit the variable baseUrl with the one you got from your deployment.
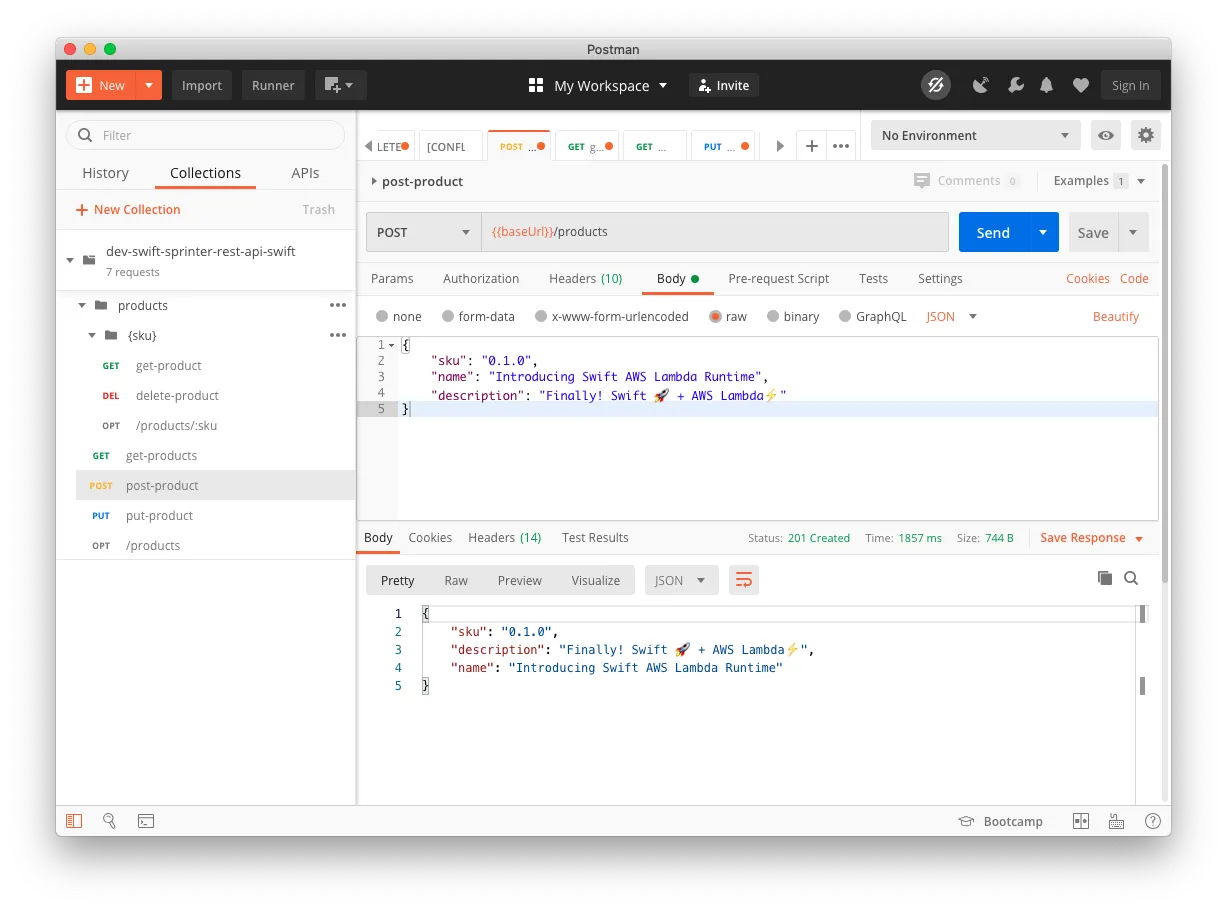
Test the API.
Once you’ve finished, you can remove the deployment by launching:
./remove.sh
Code Review
The Swift code implements the lambdas using the Apple Swift AWS Lambda Custom Runtime and AWS SDK Swift.
main.swiftruns the lambdaProduct.swiftis the Swift struct to define the data model:
public struct Product: Codable {
public let sku: String
public let name: String
public let description: String public var createdAt: String?
public var updatedAt: String?
}
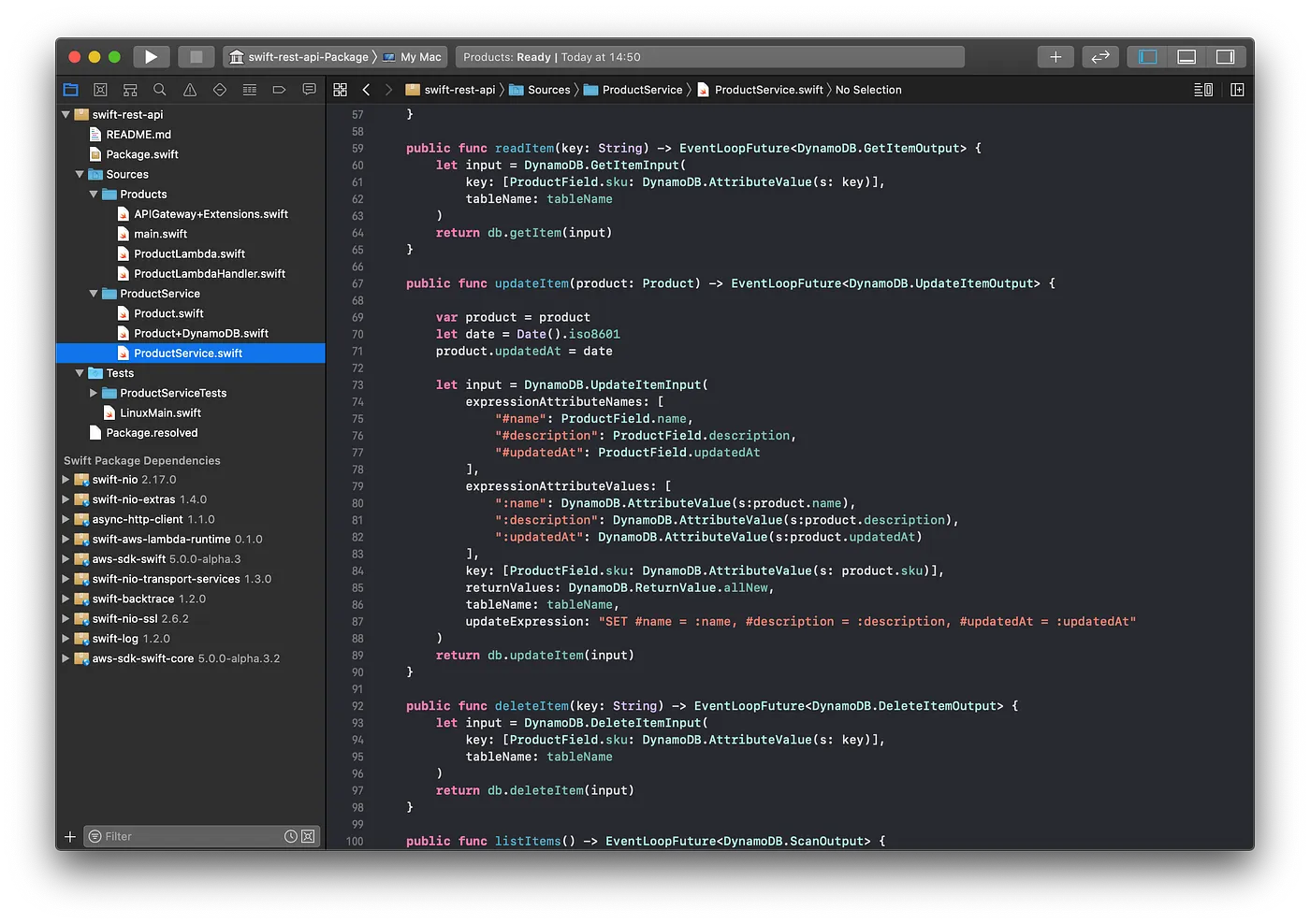
ProductLambda.swiftconfigures the DynamoDB client, which shares thehttpClientinstance with the Lambda RuntimeProductLambdaHandlerimplements the code required by the lambdas. Each lambda run only the implementation specified by the lambdaHandlerconverting the inputAPIGateway.SimpleRequestto anAPIGateway.Response.

- The lambda handlers (
Create,Read,Update,Delete List) are implemented to use the event payload and to return a result containing the desired response (or an error) - All the internal asynchronous calls are defined using the NIO
[EventLoopFuture](https://apple.github.io/swift-nio/docs/current/NIO/Classes/EventLoopFuture.html) ProductServiceabstracts the way the lambda interacts with the DynamoDB API, hiding details related to the underlying API
Conclusion
I hope to have generated some curiosity about server-side Swift and serverless. If you’re interested in the history of how this hard work started in December 2018, you can have a look at the Swift forums.
Check out the GitHub repository, and feel free to experiment. I look forward to seeing something nice!
Thanks for reading.
